
- Computer Fundamentals
- Computer - Home
- Computer - Overview
- Computer - Advantages & Disadvantages
- Computer - Classification
- Computer - Applications
- Computer - History and Evolution of Computers
- Computer - System Characteristics
- Computer - Origins
- Computer - Generations
- Computer - Types
- Computer - Components
- Computer - CPU
- Computer - Input Devices
- Computer - Output Devices
- Computer - Memory Units
- Computer - Hardware
- Computer - Motherboard
- Computer - RAM
- Computer - Read Only Memory
- Computer - Software
- Computer - Software Types
- Computer - Data Storage and Memory
- Computer - Memory
- Computer - Internet and Intranet
- Computer - Internet
- Computer - Extranet
- Computer - Websites
- Computer - Spread Sheet
- Computer - Power Presentations
- Computer - Ports
- Computer - Number System
- Computer - Number Conversion
- Computer - Data and Information
- Computer - Networking
- Computer - Operating System
- Computer - Keyboard Shortcut Keys
- Computer - Antivirus
- Computer - How to Buy?
- Computer - Available Courses
- Computer Useful Resources
- Computer - Quick Guide
- Computer - Useful Resources
- Computer - Discussion
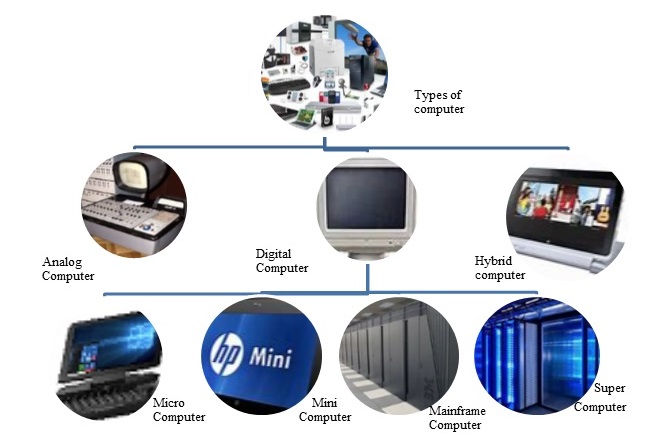
Computer - Types
The types of computer are as follows −
- Analogue computer
- Digital computer
- Micro computer
- Mini computer
- Mainframe computer
- Super computer
- Hybrid computer
Digital computers are further categorised as follows −
Analogue computer
An analog or analogue computer is a computer which processes analogue data. It processes and represents data using continuous signals such as voltage, current, or physical dimensions. The analogue computers were used during 1950s–1960s. Analogue data is not discrete; it is continuous. Pressure, temperature, voltage, speed, and weight are examples of such data. Analogue computers are most widely used in aircraft, ships, submarines, and daily appliances like refrigerator, speedometer, etc.
Types of Analogue Computers
Different types of analogue computers are as −
Mechanical Analogue Computers − These computers were using physical mechanisms like gears, levers, and rotating disks to model and solve mathematical equations. Example - analyser.
Electrical Analogue Computers − These computers were used electrical circuits to represent and solve mathematical equations. Example - Spectrometer, oscilloscope.
Optical Analogue Computers − These computers were used light and optics for computation. Example - Norden bombsight.
Analogue-Digital Hybrid Computers − These computers were the combination of analogue and digital computers so that they can process both continuous and discrete data to make them versatile for various applications like Petrol pumps, which contain a processor that converts fuel flow measurement into quantity and price.Example - Hycomp 250.
Now a day, analogue computers have replaced by digital computers. However, analogue computers are still in use where continuous data processing or simulation of physical systems is required.
Digital Computer
The digital computers are the type of computers that uses discrete data to perform computations. The most common type of computers used today is digital computers.
Personal computers, smartphones, servers and supercomputers are some of the examples of digital computers.
Digital computers are further categorised as follows −
Microcomputer − it is a type of computer which is smaller in size and less powerful than mainframe and minicomputer systems. Microcomputers are used in personal computing, office tasks, and small-scale computing applications.
Minicomputer − minicomputer is a computer that falls between mainframe computers and microcomputers. It is smaller than mainframe computers but larger than microcomputers. These computers are used for personal use for computing, and data management.
Mainframe Computer − Mainframe computers are powerful than minicomputer. These computers are used in E-business, banking, stock exchange, railway and airlines ticketing, and research centers.
Super computer − A supercomputer is a highly powerful computer. These computers are specially designed to solve complex computational problems. A supercomputer may use for space investigation, Atomic weapons, Genetic engineering, Military, Weather forecasting, simulations, data analysis.
Hybrid Computer
The hybrid computer is a type of computer that combines the functionalities of both digital and analogue computers. The primary aim of hybrid computer’s design is to do highly intricate computations. A hybrid computer has the capability to address the computational needs of large-scale organisations by effectively solving logical and technical computations, and also provides efficient processing of differential equations.
Followings are the key features of hybrid computers −
Analogue and Digital Components − Hybrid computers integrate the functionalities of both digital and analogue computers. This allows to process continuous signals from the physical world and performs digital computations.
Fast Data Conversion − Hybrid computers can convert analogue data into digital format efficiently. This process enables to process real-world data and make fruitful decisions based on processed outcomes.
High-Speed Processing − Hybrid computers are highly computational devices which do numerical calculations, making them suitable for tasks requiring complex mathematical operations and simulations.
Real-time Analysis − The hybrid computers excel in real-time analysis of continuous data.
Complex Simulations − Hybrid computers are used in scientific research and engineering simulations that necessitate the combination of mathematical modelling with integration of real-world data.
Accuracy and Precision − The hybrid computer gives accuracy and precision in calculations, ensuring reliable results for different applications.
Customization − Adjusting the proportion of analogue to digital components in hybrid computers allows them to be specialised for use in a variety of different applications.
Control Systems − Control systems in industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive, which require real-time data processing and precise control, frequently make use of hybrid computers because to their versatility and low power consumption.
Scientific Research − They are useful tools in scientific study, particularly in subjects like as physics, chemistry, and biology, where simulations using both continuous and discrete data are required. This is especially true of the domains of physics, chemistry, and biology.
Medical Imaging − In medical imaging procedures, such as the processing of data from devices like MRI and CT scanners, which involve both continuous and discrete data, hybrid computers play an important role. One example of this is the processing of MRI and CT scan data.
Weather Prediction − For the purpose of modelling the weather, hybrid computers are used in the field of meteorology. This is due to the fact that weather patterns require both on-going physical processes and intricate numerical models.
Complex Calculations − Hybrid computers can be useful in different kinds of work, including simulations of nuclear reactors and studies of fluid dynamics, which both combine real-time analysis and numerical computations.
Optimization Problems − Hybrid computers are used for solving optimization problems that require both continuous adjustments and discrete decisions.
Energy Efficiency − Hybrid computers may be more energy-efficient than digital computers because they can outsource some computations to analogue components, which may be more power-efficient for specific duties.
To Continue Learning Please Login